Electrical Safety Tips- Consumers’ Safety Guidelines for Electricity
Electrical Safety Tips for Every Fidel of Life – Save your Life
Electricity is a powerful energy source, but it can also be dangerous. In this video, we’ll cover the basics of electricity, safety tips, and the role of electrical engineers. Plus, we’ll explore how electricity affects the body and discuss safety measures during activities like Hajj.
Understanding leakage current, the functionality of electrical safety devices, and following safety tips are essential components of maintaining a safe electrical environment. Whether dealing with load variations or everyday electrical tasks, practicing awareness and caution ensures the well-being of both individuals and property.

Stay informed, stay safe! Stay safe by understanding electricity, following safety tips, and implementing protective measures. Whether you’re working with circuits or going about your day, awareness and caution are key. Stay informed, stay safe!
Electrical Safety Basics
Importance of Electrical Safety
Understanding and following safety guidelines is crucial to avoid accidents and injuries related to electricity.
What is Electricity?
Electricity is a type of energy that moves slowly from one place to another, and it needs a power source like generating stations. Electronic devices follow conductors like wires in a closed circuit.
Elements of Electrical Transmission
- Current Circuit
- Resistance Conductors
- Grounding Insulators
Electrical Engineers and Safety Hazards

Roles of Electrical Engineers
Learn about the two main types of electrical engineers, their roles, and how they deal with safety hazards.
Understanding Electrical Shocks
Explore direct and indirect electrical shocks and factors that determine their severity, such as current path, amount, and duration.
Impact of Electrical Shocks on the Body
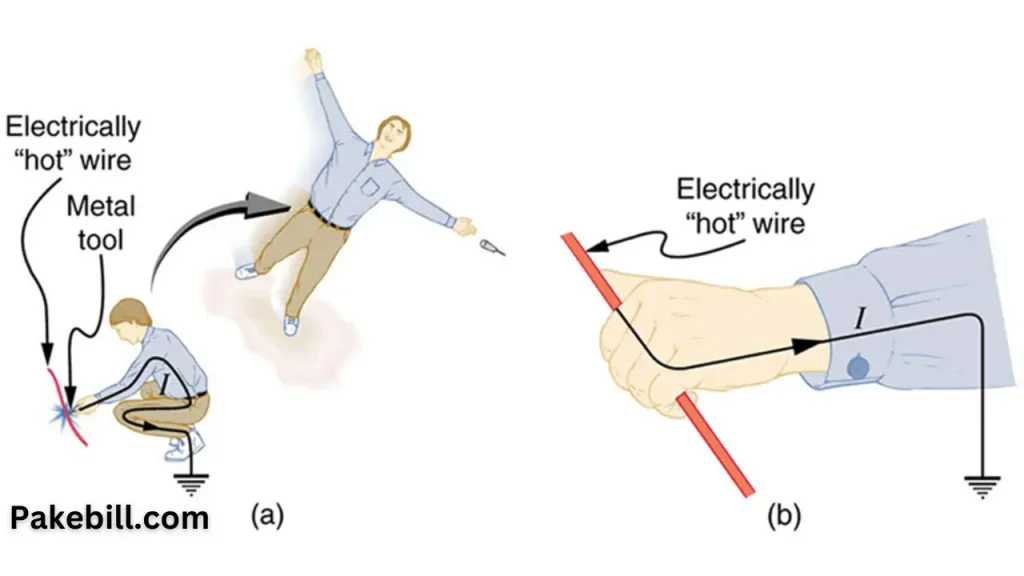
Critical Body Passes
Discover the pathways of electrical current through the body and how they impact the severity of an electric shock.
Dangers of Electrical Shocks
Learn about the potential dangers of electrical shocks, including paralysis and heart-related issues, based on the amount of current.
Protective Measures and Safety Tips
Common Electrical Hazards
Understand the risks associated with exposed electrical parts, improper wiring, insufficient insulation, and damaged power tools.
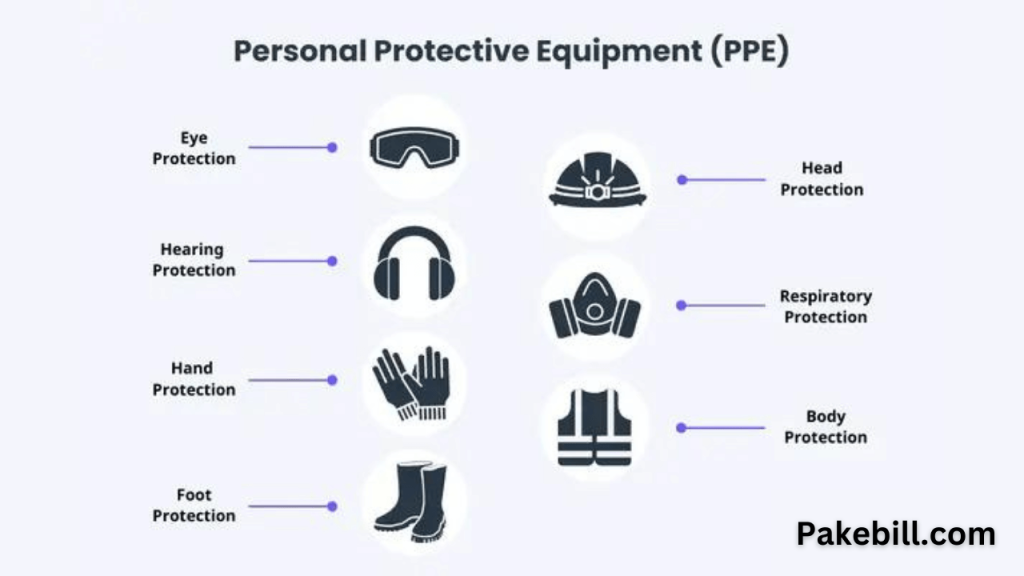
Protective Measures
Get practical tips on staying safe, including proper grounding, the use of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI), insulation, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Current Load Variation
When we talk about electrical circuits, the load on the neutral wire plays a crucial role. Let’s say our neutral wire was initially handling a load of 20 amperes. Now, imagine that the load has increased, and the neutral wire is now managing 30 milliamperes. This increase in load impacts the earth connection, leading to a phenomenon known as leakage current.
Sensing through CBCT
To comprehend and manage this leakage current, electrical safety devices come into play. One such device is the Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCB). It utilizes a component called the Core Balance Current Transformer (CBCT) to sense any abnormal increase in the current flow.
Tripping of RCB
Once the CBCT detects an increased leakage current, it sends this information to the relay operating coils. The relay, in turn, triggers the Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCB), causing it to trip. This tripping action is a safety measure that effectively disconnects the current flow, preventing potential hazards associated with the increased leakage.
Electrical Safety Tips for Every Fidel of Life
Top 10 Electrical Safety Tips for Homeowners
- Cut the Power: Always disable power before electrical work.
- Fire Extinguisher: Keep an electrical fire-rated extinguisher.
- Multiple Outlets: Avoid overloading outlets.
- Outlet Checks: Regularly monitor outlet temperatures.
- Child-Proof Outlets: Install automatic shut-off covers.
- Investigate Flickering Lights: Promptly address loose wires.
- Install AFCIs: Prevent fires with Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters.
- Avoid Long-Term Extension Cord Use: Use them temporarily.
- Install GFCIs: Enhance safety in kitchens and bathrooms.
- Leave Electrical Work to Professionals: Prioritize professional expertise.
Electrical Safety Tips for School, College, and University
- Power Precautions: Always turn off power before conducting electrical work on campus.
- Emergency Readiness: Ensure the availability of electrical fire-rated extinguishers.
- Outlet Management: Avoid overloading outlets in classrooms and common areas.
- Regular Checks: Periodically inspect outlet temperatures across campus facilities.
- Child-Safe Campuses: Install child-proof outlet covers with automatic shut-off features.
- Prompt Issue Resolution: Investigate and address flickering lights or any electrical concerns promptly.
- Fire Prevention Measures: Install Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) to prevent electrical fires.
- Temporary Extension Cord Use: Limit the use of extension cords to temporary solutions in educational spaces.
- Enhanced Safety in Critical Areas: Install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in laboratories and workshops.
- Professional Electrical Services: Always rely on professional electricians for any electrical work on campus premises.
Electrical Safety Tips for Office and Hospitals

- Power Protocol: Prioritize turning off power before conducting any electrical maintenance or work.
- Fire Safety Measures: Ensure the presence of electrical fire-rated extinguishers in offices and hospital facilities.
- Outlet Management: Avoid overloading outlets to maintain a safe and efficient working environment.
- Routine Inspections: Conduct regular checks on outlet temperatures and wiring integrity.
- Child-Proof Precautions: Install child-proof outlet covers with automatic shut-off features in pediatric units and child-friendly areas.
- Swift Issue Resolution: Address flickering lights or electrical issues promptly to prevent disruptions.
- Fire Prevention in Offices: Install Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) to minimize fire risks in office spaces.
- Temporary Use of Extension Cords: Limit the use of extension cords to temporary solutions and ensure proper installation.
- Enhanced Safety in Critical Areas: Implement Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in medical laboratories and high-risk zones.
- Professional Electrical Services: Engage licensed electricians for all electrical work to ensure safety and compliance in office and hospital settings.
Electrical Safety Tips for Workplace Safety
- Power Down Before Work: Always turn off power before conducting any electrical maintenance or modifications.
- Fire Safety Preparedness: Keep electrical fire-rated extinguishers strategically placed in the workplace.
- Outlet Management: Avoid overloading outlets to prevent electrical hazards in the workplace.
- Regular Inspections: Perform routine checks on outlet temperatures and wiring conditions to identify potential issues.
- Child-Proof Outlets: Install child-proof outlet covers with automatic shut-off features in areas accessible to children.
- Prompt Issue Resolution: Address flickering lights or electrical problems swiftly to maintain a safe working environment.
- Install AFCIs: Install Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) to minimize the risk of fires in the workplace.
- Temporary Extension Cord Use: Limit the use of extension cords to temporary solutions and ensure proper installation.
- GFCIs in Sensitive Areas: Implement Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in areas where electrical equipment is used intensively.
- Professional Electrical Services: Engage licensed electricians for any electrical work in the workplace to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
By integrating these tailored electrical safety tips into various settings, we contribute to creating environments that prioritize safety and well-being. Remember, a proactive approach to electrical safety benefits everyone. Stay safe!
Library Electrical Safety: Easy Guidelines
Master easy yet detailed guidelines for electrical safety in libraries, from turning off equipment to distinguishing ECB from RCB.
Difference Between ECB and RCB
Full Form and Name
- ECB (Earth Circuit Breaker): This term is commonly used to refer to a circuit breaker that is primarily focused on managing issues related to the earth connection.
- RCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker): Also known as a Residual Current Device (RCD), it is specifically designed to detect and manage any residual or leakage current.
Operation and Sensing
- ECB: Historically, Earth Circuit Breakers were often voltage-operated, relying on the presence of current or part current in close proximity.
- RCB: Residual Current Circuit Breakers are current-operated, capable of sensing leakage current even without direct current proximity.
Functionality Requirement
- ECB: Effective functioning often depends on a good earth connection. If the earth connection is not optimal, the performance may be compromised.
- RCB: Residual Current Circuit Breakers can function well even without a perfect earth connection. They focus more on the detection of leakage current.
Sensitivity to Current
- ECB: Requires the presence of current or part current nearby for operation. It may not operate correctly if there is no current in the vicinity.
- RCB: Operates based on the detection of leakage current, irrespective of whether current is present nearby or not.
Historical Naming
- ECB: Historically referred to as a Voltage Operated Circuit Breaker, highlighting its reliance on voltage-related factors.
- RCB: Also known as a Current Operated Residual Current Circuit Breaker or Device, underlining its focus on managing residual or leakage currents.
Advantages of Following Electrical Safety Tips
- Prevents Accidents: Reduces the risk of accidents and injuries related to electricity.
- Shields Against Shocks: Protects against electrical shocks through grounding and insulation.
- Mitigates Fire Hazards: Prevents electrical fires by addressing wiring and circuit issues.
- Extends Equipment Lifespan: Ensures correct usage and maintenance, prolonging equipment life.
- Enhances Workplace Safety: Promotes a safer work environment and prevents environmental damage.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Adheres to local and national safety regulations.
- Reduces Downtime: Minimizes electrical failures, reducing disruptions and downtime.
- Safeguards Electronic Devices: Protects devices from power-related damage.
- Saves Costs: Prevents costly repairs, replacements, and legal liabilities.
- Fosters Safety Culture: Creates awareness, encouraging a culture of safety and responsibility.
Disadvantages of Unfollowing Electrical Safety Tips
- Increased Accident Risks: Raises the likelihood of accidents and injuries due to negligence.
- Higher Chance of Shocks: Elevates the risk of electric shocks by ignoring safety precautions.
- Greater Fire Hazard: Escalates the potential for electrical fires with unchecked issues.
- Shortened Equipment Lifespan: Accelerates wear and tear, reducing the lifespan of electrical equipment.
- Compromised Workplace Safety: Undermines the overall safety of the workplace environment.
- Risk of Legal Consequences: Exposes individuals and organizations to legal liabilities for non-compliance.
- Increased Downtime: Heightens the likelihood of electrical failures, leading to increased downtime.
- Damage to Electronic Devices: Puts electronic devices at a higher risk of damage from power-related issues.
- Higher Financial Costs: Incurs additional costs for repairs, replacements, and potential legal consequences.
- Weakens Safety Culture: Undermines efforts to foster a culture of safety, responsibility, and awareness.
Conclusion
Understanding leakage current, electrical safety devices, and implementing safety tips are vital for a secure environment. Whether facing load variations or daily electrical tasks, awareness and caution ensure well-being. Stay informed, stay safe. Empower yourself with this guide, applicable across life’s diverse domains. Stay safe, stay enlightened!






